Table of Contents
Key takeaways
- Green hydrogen, a cornerstone: Green hydrogen is a clean and innovative energy source, marking a pivotal step towards a sustainable future in the global energy transition.
- Eco-friendly production: Green hydrogen is obtained through water electrolysis, using electricity sourced from renewable sources, setting it apart from its less eco-friendly counterparts.
- Significant environmental benefits: Green hydrogen reduces CO2 emissions and finds applications in transportation, energy storage, and industry, contributing to the challenging decarbonization of key sectors.
Green hydrogen is emerging as a cornerstone in the global energy transition. As a clean and innovative energy source, it marks a decisive turn towards a sustainable future. This article explores the genesis, applications, and environmental benefits of green hydrogen, while highlighting its challenges and potential in tomorrow’s energy landscape.
What is green hydrogen?
Green hydrogen represents a major advance in the quest for clean and sustainable energy. Unlike its less eco-friendly counterparts, green hydrogen is produced in an environmentally friendly manner, positioning it as a key player in the energy transition.
Definition and production of green hydrogen
Green hydrogen is obtained through the electrolysis of water, a process that separates oxygen from hydrogen using electricity. The revolutionary aspect of this method lies in its electricity source: if it comes from renewable sources such as wind or solar, hydrogen production becomes entirely green. This process offers an alternative to traditional hydrogen production methods, often dependent on fossil fuels and generating greenhouse gases.
Comparison with other types of hydrogen
It is crucial to differentiate green hydrogen from its less ecological counterparts. For example, grey hydrogen is produced mainly from methane, with substantial CO2 emissions. Blue hydrogen, although also derived from fossil sources, involves carbon capture and storage to minimize emissions. Nevertheless, green hydrogen stands out as the most sustainable and ecological option, thanks to its greenhouse gas emission-free production.
Environmental benefits
Green hydrogen plays a significant role in reducing CO2 emissions. Its use as a renewable energy source and its energy storage potential offer a viable alternative to fossil fuels. This is particularly relevant in sectors where decarbonization is challenging, such as heavy transport and industry. Adopting green hydrogen can therefore lead to a considerable reduction in the global carbon footprint, marking an essential step towards a sustainable energy future.
Applications of green hydrogen in the energy sector
With its capacity to revolutionize various sectors, green hydrogen plays a crucial role in the field of energy. Its versatility and compatibility with existing technologies make it a key element of the energy transition.
Use in transport
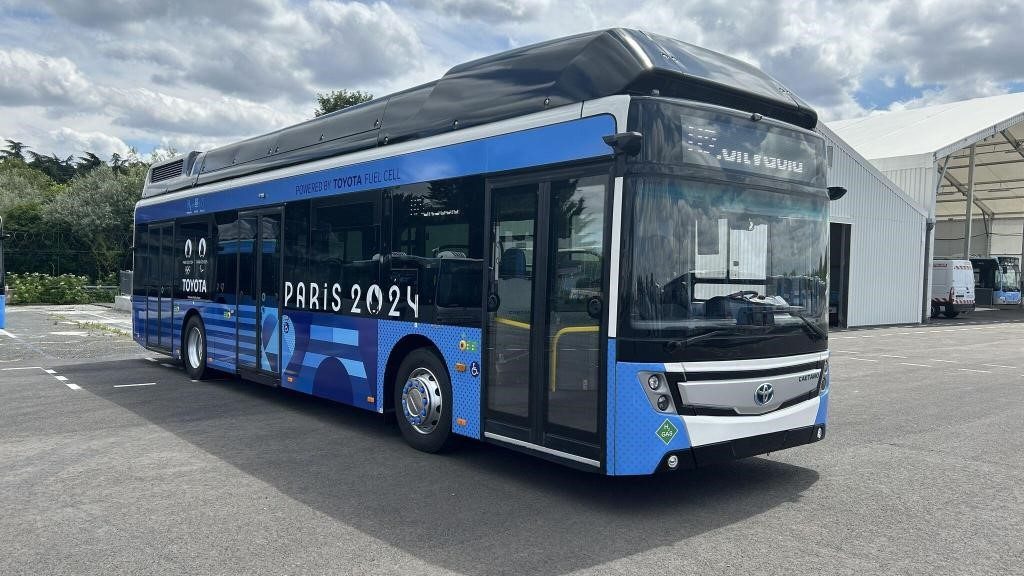
In the transport sector, green hydrogen is a fuel of the future. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, such as cars, buses, and trains, offer a zero-emission alternative. These vehicles convert hydrogen into electricity, producing only water as waste. They offer range and recharge times comparable to traditional vehicles, while drastically reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The growing adoption of these vehicles demonstrates the potential of green hydrogen in replacing fossil fuels.
Role in energy storage
Energy storage is another area where green hydrogen excels. It can be used to store excess energy produced by renewable sources, such as wind or solar. The produced hydrogen can be converted back into electricity or used in other applications, offering a flexible and sustainable energy storage solution. This ability to store large amounts of energy over extended periods is essential for stabilizing electrical grids and integrating more renewable energies.
Potential in industry
Finally, green hydrogen has significant potential in various industrial sectors. In the steel industry, it can replace fossil fuels to reduce CO2 emissions. In the chemical sector, it is used in the production of essential chemicals, such as ammonia, in a more sustainable way. The use of green hydrogen in these industrial processes is a step towards a cleaner and greener industry.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
The development and adoption of green hydrogen, although hopeful, face significant technical and economic challenges that must be overcome to realize its full potential in the future of energy.
Technical and economic problems
One of the main obstacles to the expansion of green hydrogen is its high production cost. Currently, water electrolysis requires a large amount of electricity, often expensive, especially if it comes from renewable sources. Moreover, the energy efficiency of converting electricity to hydrogen and then back to electricity can be low, raising questions about efficiency. Furthermore, existing infrastructures, such as transport pipelines and refueling stations, are insufficient for large-scale integration of green hydrogen, thus requiring significant investments.
Government initiatives and policies
In response to these challenges, various governments and international organizations have launched initiatives to promote green hydrogen. These initiatives include subsidies for research and development, incentives for companies using green hydrogen, and policies aimed at facilitating the integration of hydrogen into existing energy systems. These efforts are crucial for reducing costs and improving the efficiency of green hydrogen technology.
Future Projections
Despite these challenges, the future prospects of green hydrogen are promising. Technological advances continue to reduce production costs and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, the growing demand for clean and sustainable energy solutions is stimulating investment and innovation in this sector. It is expected that, in the coming years, green hydrogen will become increasingly competitive and play a major role in the global energy transition, offering a viable solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
Case studies and successes
The global success of green hydrogen is evidenced through various innovative projects. Countries like Germany, Japan, and South Korea stand out for their ambitious initiatives, integrating green hydrogen into their energy mix. For example, in Germany, projects like the Hydrogen Council are driving the use of hydrogen in transport and industry, marking a decisive turn towards a decarbonized economy. In Japan, green hydrogen is at the heart of the national strategy for a low-carbon society, with significant investments in fuel cell technology. These examples illustrate the global commitment to green hydrogen and its essential role in the global energy transition, revealing its immense potential and diverse applicability.