Hydrogen will be inevitable in air transportation
According to the Hydrogen In Aviation alliance, HIA, which includes Airbus, Easyjet, Rolls-Royce and other partners, SAFs are...
An odorless, colorless gas
The lightest chemical element
in the Universe, present in
abundance
Higher energy density (in mass) than fossil fuels
A fuel used for rockets because of its high energy content
Jules VERNE – 1875
The first experiments with hydrogen date back to the 1800s.
In the 19th century, dirigible balloons were powered by hydrogen.
Rockets are already fueled by hydrogen, which is much more efficient and powerful than kerosene.

At present, hydrogen is mainly used in refining and in the production of ammonia and nitrogen fertilizers.
Its uses are set to expand considerably over the coming decades.

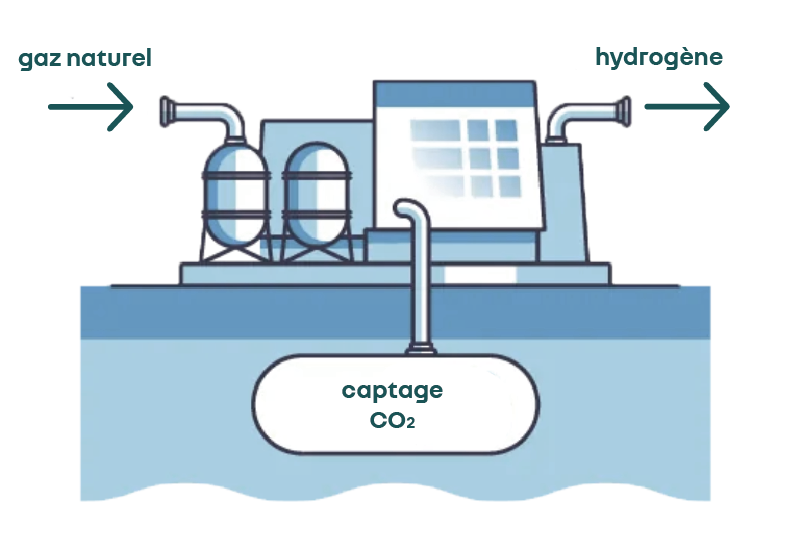
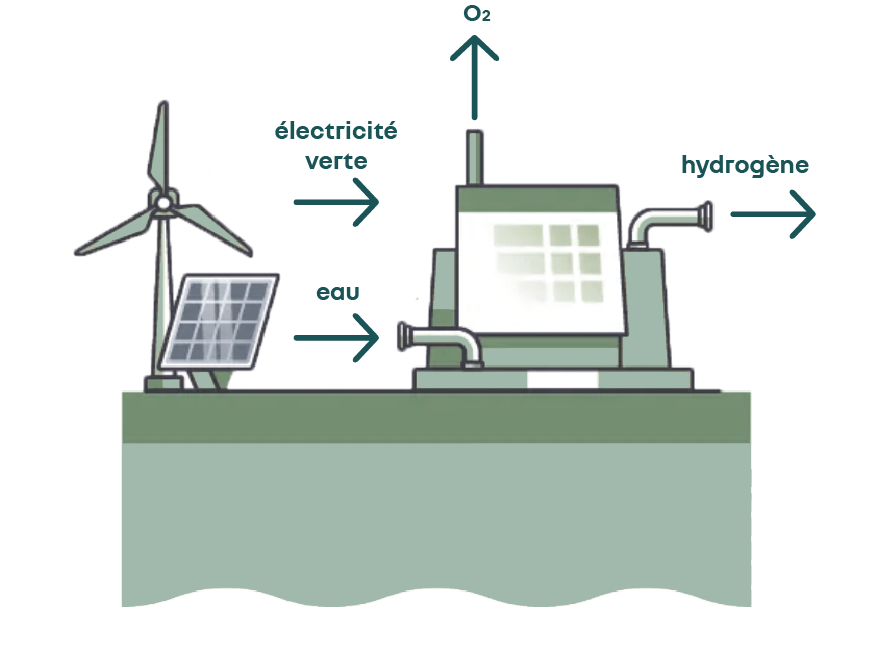
So far, hydrogen had to be produced; it was inconceivable to find it in its natural state. It was therefore considered as an “energy carrier” rather than a “resource”.
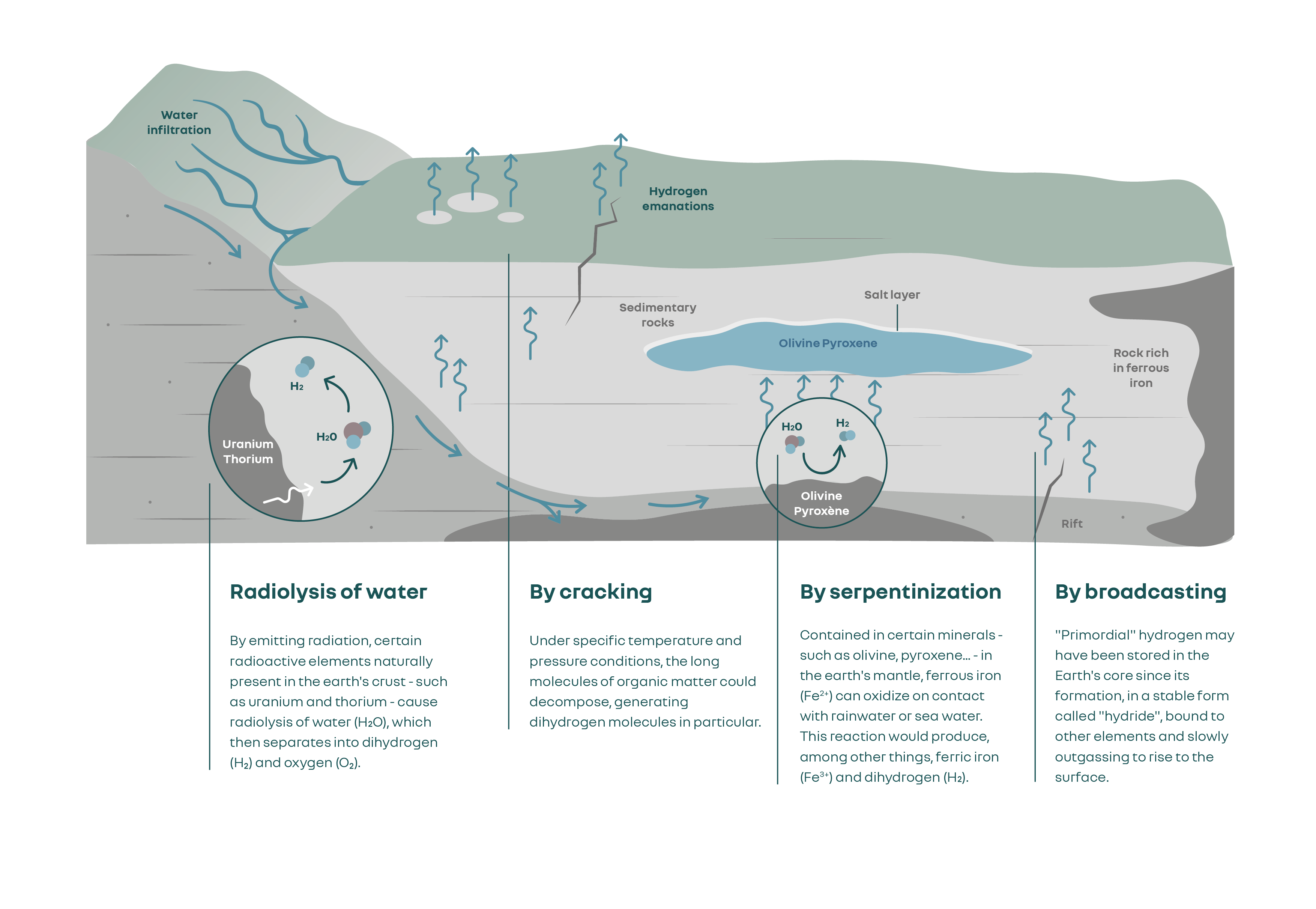
This certainty is being challenged by the recent discovery, in different parts of the world, of hydrogen in its molecular form. Just as our subsurface contains fossil energies such as coal, gas, and oil, it is now established that it also contains hydrogen in its natural state and potentially in substantial quantities.
While current methods of hydrogen production are polluting and costly methods, the exploitation of natural hydrogen constitutes a real energy revolution: it is not only an innovative mode of production but also clean and economically viable with a cost 6 times lower than for green hydrogen.
Various geological processes could be responsible for a natural production of hydrogen beneath the Earth’s surface (illustration from the article “Hidden Hydrogen” published in the magazine Science).
Research and exploration work has started in various parts of the world, particularly in Australia, the United States, and France.
According to the Hydrogen In Aviation alliance, HIA, which includes Airbus, Easyjet, Rolls-Royce and other partners, SAFs are...
